Abstract
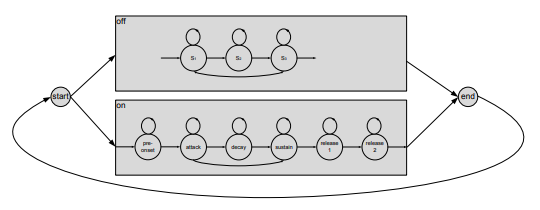
Automatic music transcription is a challenging task that has been the topic of many research groups since 1977. The problem has been addressed in several manners and suitable results were obtained for the monophonic case, where a single note is played at a time. Still, the transcription of real-world polyphonic music with arbitrary instruments, genre and tempi suffers from many unsolved problems. The two key sub-problems in automatic music transcription necessary to obtain a note-level parameter representation of a musical piece are polyphonic pitch estimation and notes’ onset detection. Both tasks are addressed in this thesis for real-world music. Effective signal representations are proposed that adapt the properties of music signals. The spectral characteristics are described with a semitone spectrogram that receives enhanced time/frequency resolution through the use of a multiresolution DFT and instantaneous frequency estimation. Nonharmonic signal components are suppressed using RASTA processing. The temporal characteristics are modeled in complex domain, taking envelope and frequency continuity conditions into account. An iterative approach is proposed for the polyphonic pitch estimation that detects the predominant F0 in a signal and uses harmonic spectrum estimation to extract it, before the estimation is continued with the residual. The onset and duration detection of each note is resolved through temporal properties of the signal. In addition, Hidden Markov Models are used to model each note as a distinct event with both, spectral and temporal characteristics simultaneously to determine its pitch, onset and offset. To further enhance the results achievable with the methods based on signal properties, musical knowledge is used, namely the musical key to find probable notes in a song, and musical meter to define probable on- and offset positions. The evaluation of the proposed methods is carried out on a database of acoustic recordings, whose reference transcription are obtained through force alignment with midi files. Note precision and recall rates above 60% are achieved, together with a temporal accuracy of 40%.